Alexandre Mottrie, Elio Mazzone, Peter Wiklund, Markus Graefen, Justin W Collins, Ruben De Groote, Paolo Dell’Oglio, Stefano Puliatti, Anthony G Gallagher
- PMID: 33251703
- PMCID: PMC8359192
- DOI: 10.1111/bju.15311
Abstract
Objective: To develop and seek consensus from procedure experts on the metrics that best characterise a reference robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) and determine if the metrics distinguished between the objectively assessed RARP performance of experienced and novice urologists, as identifying objective performance metrics for surgical training in robotic surgery is imperative for patient safety.
Materials and methods: In Study 1, the metrics, i.e. 12 phases of the procedure, 81 steps, 245 errors and 110 critical errors for a reference RARP were developed and then presented to an international Delphi panel of 19 experienced urologists. In Study 2, 12 very experienced surgeons (VES) who had performed >500 RARPs and 12 novice urology surgeons performed a RARP, which was video recorded and assessed by two experienced urologists blinded as to subject and group. Percentage agreement between experienced urologists for the Delphi meeting and Mann-Whitney U- and Kruskal-Wallis tests were used for construct validation of the newly identified RARP metrics.
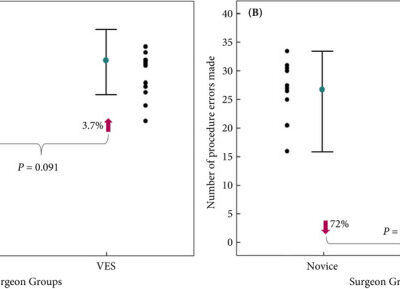
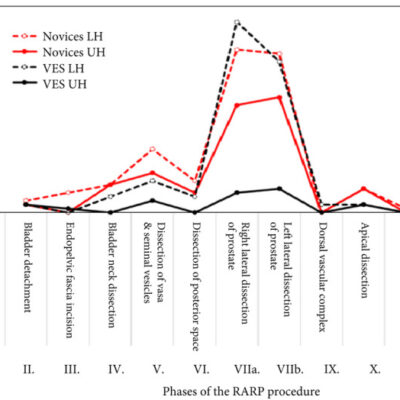
Results: At the Delphi panel, consensus was reached on the appropriateness of the metrics for a reference RARP. In Study 2, the results showed that the VES performed ~4% more procedure steps and made 72% fewer procedure errors than the novices (P = 0.027). Phases VIIa and VIIb (i.e. neurovascular bundle dissection) best discriminated between the VES and novices.
Limitations: VES whose performance was in the bottom half of their group demonstrated considerable error variability and made five-times as many errors as the other half of the group (P = 0.006).
Conclusions: The international Delphi panel reached high-level consensus on the RARP metrics that reliably distinguished between the objectively scored procedure performance of VES and novices. Reliable and valid performance metrics of RARP are imperative for effective and quality assured surgical training.
Keywords: #EndoUrology; #PCSM; #Prostate Cancer; #uroonc; construct validation; proficiency-based metrics; proficiency-based training; robot-assisted radical prostatectomy; surgical training.
© 2020 The Authors BJU International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of BJU International.
Conflict of interest statement
Alexandre Mottrie reports grants from Intuitive, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from ORSI Academy, outside the submitted work; Justin W Collins reports grants from Medtronic, personal fees from Medtronic, personal fees from Intuitive Surgical, personal fees from CMR Surgical, outside the submitted work; Elio Mazzone, Peter Wiklund, Markus Graefen, Paolo Dell’Oglio, Ruben De Groote, Stefano Puliatti and Anthony G Gallagher certify that all their conflicts of interest, including specific financial interests and relationships and affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript (e.g. employment/affiliation, grants or funding, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, royalties, or patents filed, received, or pending), are the following: None.