From the first year in the specialization school (2012), Dr. Puliatti was involved in the robotics surgery team. Prof. Giampaolo Bianchi was among the first in Italy in 2007 to believe in this futuristic technology by creating a hyper-specialized team. After 6 years of surgical activity in Modena, from 2019 to 2021 Dr. Puliatti spent two and a half years in Belgium carrying out robotic surgery activities together with Prof. Alex Mottrie, considered worldwide “top expert” for robotic surgery in urological field, inventor of specific techniques, innovator and surgeon of excellence.
Robotic surgery
In this period, Dr. Puliatti has become hyperspecialized in robotic prostate and kidney surgery and has learned the use of various robotic systems.
Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy
Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy is performed to treat organ-confined prostate cancer. This is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in men.
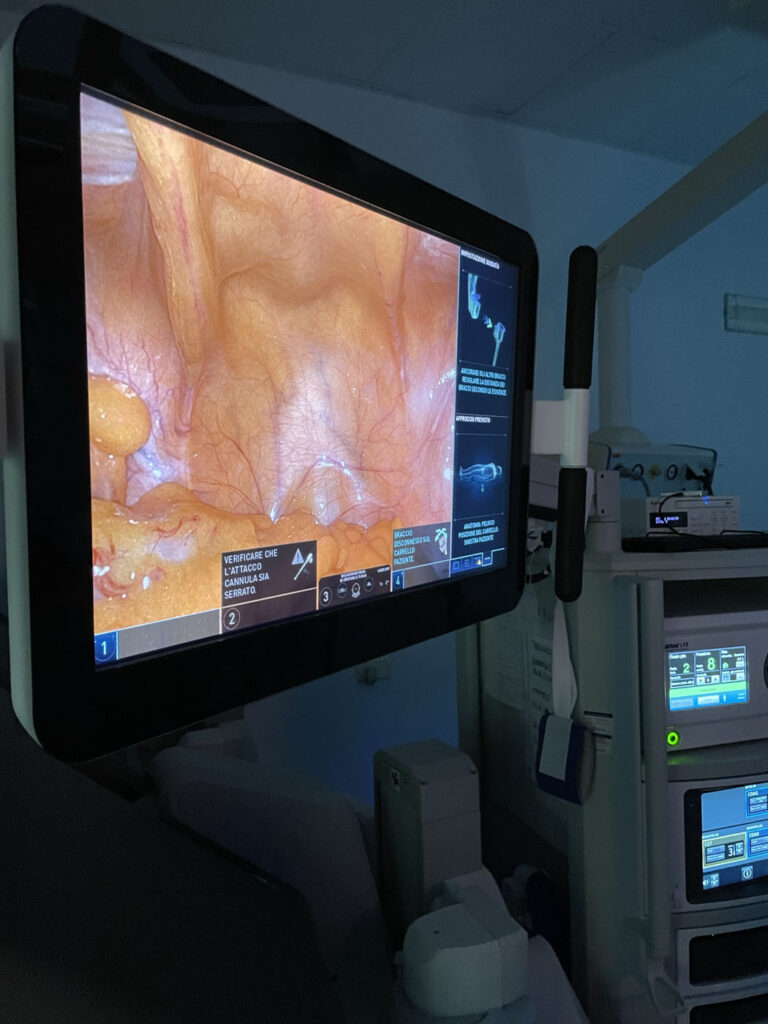
Robotic surgery represents the “gold standard” of surgical treatment of this neoplasm. In fact, it allows a shorter hospital stay, lower risks of bleeding, less pain, and can allow better aesthetic and functional results in terms of preservation of continence and sexual potency. Robotic surgery allows the surgeon a detailed and three-dimensional view of the anatomical structures. In addition, it provides 7 degrees of motion versus the 4 offered by traditional laparoscopy. This results in an accurate and precise dissection with the use of millimetric instruments.
The goal of this surgery is to treat the patient by removing the tumour while preserving the pre-existing quality of life as much as possible.
RADICAL NEPHRECTOMY AND ROBOT-ASSISTED NEPHROURETERECTOMY
Kidney tumors, renal pelvis and ureter tumors represent extremely dangerous pathologies. Often these cancers present themselves without signs or symptoms and are diagnosed incidentally in tests performed for other reasons. Sometimes these lesions require the removal of the entire kidney or kidney and ureter until it enters the bladder. Robotic surgery is also used for the execution of these procedures.This technology allows to obtain excellent aesthetic results, the reduction of postoperative pain and hospital stay with oncological outcomes comparable to those obtained in open surgery.
ROBOT-ASSISTED RENAL TUMORECTOMY
When the size and position of the neoformation allow it, it is possible to remove the kidney lesion while preserving the rest of the healthy tissue. This operation is called renal tumorectomy and allows the maximum preservation of the patient’s renal function with all the resulting advantages. Robot-assisted surgery is now widely used in this area with excellent results in terms of post-operative pain reduction, hospitalization time reduction, oncological radicality. The three-dimensional vision, the enlargement of the field of vision, the precision of the movements and the wide range of tools available allow the optimization of the procedure.
OTHER ROBOT-ASSISTED INTERVENTIONS IN UROLOGICAL SURGERY
There are also other urological interventions that find multiple advantages in being performed with a robot-assisted surgical technique. Among these: pyeloplasty, bladder diverticulectomy, prostatic adenomectomy, ureteral reimplants, sacrocolpopexy and robot-assisted radical cystectomy. In general, this technology has proven to be extremely profitable to adapt to urological surgery, allowing enormous benefits for both the patient and the surgeon.
CERTIFICATES AND CERTIFICATIONS
Train the trainer certificate
The training adds the specific knowledge of robotic technology to an existing set of clinical skills. This program included theoretical and practical skill application sessions after which the individual performance was assessed. During those intensive 2 days, experience and expertise were interchanged amongst the participants and the aim of improving the teaching skills has been attained.